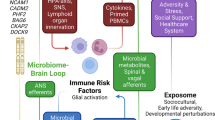
Abstract
The irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common chronic functional gastrointestinal disorder world wide that lasts for decades. The human gut harbors a diverse population of microbial organisms which is symbiotic and important for well being. However, studies on conventional, germ-free, and obese animals have shown that alteration in normal commensal gut microbiota and an increase in pathogenic microbiota—termed “dysbiosis”, impact gut function, homeostasis, and health. Diarrhea, constipation, visceral hypersensitivity, and abdominal pain arise in IBS from the gut-induced dysfunctional metabolic, immune, and neuro-immune communication. Dysbiosis in IBS is associated with gut inflammation. Gut-related inflammation is pivotal in promoting endotoxemia, systemic inflammation, and neuroinflammation. A significant proportion of IBS patients chronically consume alcohol, non-steroidal anti-inflammatories, and fatty diet; they may also suffer from co-morbid respiratory, neuromuscular, psychological, sleep, and neurological disorders. The above pathophysiological substrate is underpinned by dysbiosis, and dysfunctional bidirectional “Gut-Brain Axis” pathways. Pathogenic gut microbiota-related systemic inflammation (due to increased lipopolysaccharide and pro-inflammatory cytokines, and barrier dysfunction), may trigger neuroinflammation enhancing dysfunctional brain regions including hippocampus and cerebellum. These as well as dysfunctional vago-vagal gut-brain axis may promote cognitive impairment. Indeed, inflammation is characteristic of a broad spectrum of neurodegenerative diseases that manifest demntia. It is argued that an awareness of pathophysiological impact of IBS and implementation of appropriate therapeutic measures may prevent cognitive impairment and minimize vulnerability to dementia.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Aβ:
-
Amyloid beta
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- ALI:
-
Acute lung injury
- APP:
-
Amyloid precursor protein
- BBB:
-
Blood–brain barrier
- BOLD:
-
Blood oxygen level-dependent signal
- CBF:
-
Cerebral blood flow
- CD:
-
Celiac disease
- CFGD:
-
Chronic functional gastrointestinal disorders
- CgA:
-
Chromogranin A
- CRF:
-
Corticotropin-releasing factor
- CVO:
-
Circumventricular
- DLPFC:
-
Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
- ENS:
-
Enteric nervous system
- EPSC:
-
Excitatory postsynaptic currents
- GIT:
-
Gastrointestinal tract
- HC:
-
Healthy control
- HF:
-
Heart failure
- HLA:
-
Human leukocyte antigen
- IBS:
-
Irritable bowel syndrome
- IFN-γ:
-
Interferon gamma
- IFL:
-
Airflow limitation
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- IL-1ra:
-
Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- nAChR:
-
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
- NAA:
-
N-acetyl-aspartate
- NANC:
-
Non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic pathway
- NCGS:
-
Non-celiac gluten sensitivity
- NFκB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa B
- NFT:
-
Neurofibrillary tangles
- NSAID:
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatorY drug
- NTS:
-
Nucleus tractus solitarius (nucleus of the solitary tract)
- PSQI:
-
Pittsburgh sleep quality index
- REM:
-
Rapid eye movement
- SFO:
-
Subfornical organ
- tau :
-
A microtubule-associated protein
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
- VNS:
-
Vagus nerve stimulation
References
Neish AS (2009) Microbes in gastrointestinal health and disease. Gastroenterology 136:65–80
Zoetendal EG, Vaughan EE, de Vos WM (2006) A microbial world within us. Mol Microbiol 59:1639–1650
Kolling G, Wu M, Guerrant RL (2012) Enteric pathogens through life stages. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2:114
Wang Y, Gilbreath TM 3rd, Kukutla P, Yan G, Xu J (2011) Dynamic gut microbiome across life history of the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae in Kenya. PLoS ONE 6:e24767
Hooda S, Minamoto Y, Suchodolski JS, Swanson KS (2012) Current state of knowledge: the canine gastrointestinal microbiome. Anim Health Res Rev 13:78–88
Vipperla K, O’Keefe SJ (2012) The microbiota and its metabolites in colonic mucosal health and cancer risk. Nutr Clin Pract 27:624–635
Greiner T, Bäckhed F (2011) Effects of the gut microbiota on obesity and glucose homeostasis. Trends Endocrinol Metab 22:117–123
Bäckhed F (2012) Host responses to the human microbiome. Nutr Rev 70(Suppl 1):S14–S17
Cryan JF, Dinan TG (2012) Mind-altering microorganisms: the impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat Rev Neurosci 13:701–712
Tiihonen K, Ouwehand AC, Rautonen N (2010) Effect of overweight on gastrointestinal microbiology and immunology: correlation with blood biomarkers. Br J Nutr 103:1070–1078
Björklund M, Ouwehand AC, Forssten SD, Nikkilä J, Tiihonen K, Rautonen N, Lahtinen SJ (2012) Gut microbiota of healthy elderly NSAID users is selectively modified with the administration of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM and lactitol. Age (Dordr) 34:987–999
Bravo JA, Forsythe P, Chew MV, Escaravage E, Savignac HM, Dinan TG, Bienenstock J, Cryan JF (2011) Ingestion of lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:16050–16055
Costantini TW, Krzyzaniak M, Cheadle GA, Putnam JG, Hageny AM, Lopez N, Eliceiri BP, Bansal V, Coimbra R (2012) Targeting α-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in the enteric nervous system: a cholinergic agonist prevents gut barrier failure after severe burn injury. Am J Pathol 181:478–486
de Jonge WJ (2013) The Gut’s Little Brain in Control of Intestinal Immunity. ISRN Gastroenterol 2013:630159
Matteoli G, Boeckxstaens GE (2013) The vagal innervation of the gut and immune homeostasis. Gut 62:1214–1222
Foster JA, McVey Neufeld KA (2013) Gut-brain axis: how the microbiome influences anxiety and depression. Trends Neurosci 36:305–312
Collins S, Verdu E, Denou E, Bercik P (2009) The role of pathogenic microbes and commensal bacteria in irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Dis 27(Suppl 1):85–89
Collins SM, Denou E, Verdu EF, Bercik P (2009) The putative role of the intestinal microbiota in the irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Liver Dis 41:850–853
Collins SM, Surette M, Bercik P (2012) The interplay between the intestinal microbiota and the brain. Nat Rev Microbiol 10:735–742
Ducrotté P (2009) Irritable bowel syndrome: from the gut to the brain-gut. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 33:703–712
Lee BJ, Bak YT (2011) Irritable bowel syndrome, gut microbiota and probiotics. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 17:252–266
Barbara G, Zecchi L, Barbaro R, Cremon C, Bellacosa L, Marcellini M, De Giorgio R, Corinaldesi R, Stanghellini V (2012) Mucosal permeability and immune activation as potential therapeutic targets of probiotics in irritable bowel syndrome. J Clin Gastroenterol 46(Suppl):S52–S55
Hughes PA, Zola H, Penttila IA, Blackshaw LA, Andrews JM, Krumbiegel D (2013) Immune activation in irritable bowel syndrome: can neuroimmune interactions explain symptoms? Am J Gastroenterol 108:1066–1074
Bercik P, Park AJ, Sinclair D, Khoshdel A, Lu J, Huang X, Deng Y, Blennerhassett PA, Fahnestock M, Moine D, Berger B, Huizinga JD, Kunze W, McLean PG, Bergonzelli GE (2011) The anxiolytic effect of Bifidobacterium longum NCC3001 involves vagal pathways for gut-brain communication. Neurogastroenterol Motil 23(12):1132–1139
Bercik P, Collins SM, Verdu EF (2012) Microbes and the gut-brain axis. Neurogastroenterol Motil 24:405–413
Fujiwara Y, Kubo M, Kohata Y, Machida H, Okazaki H, Yamagami H, Tanigawa T, Watanabe K, Watanabe T, Tominaga K, Arakawa T (2011) Cigarette smoking and its association with overlapping gastroesophageal reflux disease, functional dyspepsia, or irritable bowel syndrome. Intern Med 50:2443–2447
Reddy YM, Singh D, Nagarajan D, Pillarisetti J, Biria M, Boolani H, Emert M, Chikkam V, Ryschon K,VacekJ, Bommana S, Atkins D, Verma A, Olyaee M, Dawn B, Lakkireddy D (2013) Atrial fibrillation ablation in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease or irritable bowel syndrome- the heart to gut connection. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 37:259–265
Kaji M, Fujiwara Y, Shiba M, Kohata Y, Yamagami H, Tanigawa T, Watanabe K, Watanabe T, Tominaga K, Arakawa T (2010) Prevalence of overlaps between GERD, FD and IBS and impact on health-related quality of life. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 25:1151–1156
Engelhart MJ, Geerlings MI, Meijer J, Kiliaan A, Ruitenberg A, van Swieten JC, Stijnen T, Hofman A, Witteman JC, Breteler MM (2004) Inflammatory proteins in plasma and the risk of dementia: the rotterdam study. Arch Neurol 61:668–672
Griffin WS (2006) Inflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. Am J Clin Nutr 83:470S–474S
Churchill L, Taishi P, Wang M, Brandt J, Cearley C, Rehman A, Krueger JM (2006) Brain distribution of cytokine mRNA induced by systemic administration of interleukin-1beta or tumor necrosis factor alpha. Brain Res 1120:64–73
Perry VH, Cunningham C, Holmes C (2007) Systemic infections and inflammation affect chronic neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Immunol 7:161–167
Zhang R, Miller RG, Gascon R, Champion S, Katz J, Lancero M, Narvaez A, Honrada R, Ruvalcaba D, McGrath MS (2009) Circulating endotoxin and systemic immune activation in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (sALS). J Neuroimmunol 206:121–124
Zhang R, Miller RG, Madison C, Jin X, Honrada R, Harris W, Katz J, Forshew DA, McGrath MS (2013) Systemic immune system alterations in early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroimmunol 256:38–42
Eikelenboom P, Zhan SS, Van Gool WA, Allsop D (1994) Inflammatory mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci 15:447–450
Eikelenboom P, van Exel E, Hoozemans JJ, Veerhuis R, Rozemuller AJ, van Gool WA (2010) Neuroinflammation—an early event in both the history and pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurodegener Dis 7:38–41
Eikelenboom P, Veerhuis R, van Exel E, Hoozemans JJ, Rozemuller AJ, van Gool WA (2011) The early involvement of the innate immunity in the pathogenesis of late-onset Alzheimer’s disease: neuropathological, epidemiological and genetic evidence. Curr Alzheimer Res 8:142–150
Eikelenboom P, Hoozemans JJ, Veerhuis R, van Exel E, Rozemuller AJ, van Gool WA (2012) Whether, when and how chronic inflammation increases the risk of developing late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 4:15
Parachikova A, Agadjanyan MG, Cribbs DH, Blurton-Jones M, Perreau V, Rogers J, Beach TG, Cotman CW (2007) Inflammatory changes parallel the early stages of Alzheimer disease. Neurobiol Aging 28:1821–1833
Agostinho P, Cunha RA, Oliveira C (2010) Neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Pharm Des 16:2766–2778
Daulatzai MA (2010) Early stages of pathogenesis in memory impairment during normal senescence and Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 20:355–367
Daulatzai MA (2010) Conversion of elderly to alzheimer’s dementia: role of confluence of hypothermia and senescent stigmata—the plausible pathway. J Alzheimers Dis 21:1039–1063
Daulatzai MA (2011) Role of sensory stimulation in the amelioration of obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Disord 2011(2011):596879
Daulatzai MA (2012) Memory and cognitive dysfunctions in Alzheimer’s disease are inextricably intertwined with neuroinflammation due to aging, obesity, obstructive sleep apnea, and other upstream risk factors. In: Costa A, Villalba E (eds) Horizons in neuroscience research. Nova Science Publishers Inc., NY, pp 69–106
Daulatzai MA (2012) Pathogenesis of cognitive dysfunction in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: a hypothesis with emphasis on the nucleus tractus solitarius. Sleep Disord 2012(2012):251096
Daulatzai MA (2012) Neuroinflammation and dysfunctional nucleus tractus solitarius: their role in neuropathogenesis of Alzheimer’s dementia. Neurochem Res 37:846–868
Daulatzai MA (2012) Quintessential risk factors: their role in promoting cognitive dysfunction and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Res 37:2627–2658
Daulatzai MA (2013) Death by a thousand cuts in Alzheimer’s disease: hypoxia: the prodrome. Neurotox Res 24:216–243
Daulatzai MA (2013) Neurotoxic saboteurs: straws that break the hippo’s (Hippocampus) back drive cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotox Res 24:407–459
Şimşek I (2011) Irritable bowel syndrome and other functional gastrointestinal disorders. J Clin Gastroenterol 45 Suppl: S86-S88
Breckan RK, Asfeldt AM, Straume B, Florholmen J, Paulssen EJ (2012) Prevalence, comorbidity, and risk factors for functional bowel symptoms: a population-based survey in Northern Norway. Scand J Gastroenterol 47:1274–1282
Dupont HL (2011) Gastrointestinal infections and the development of irritable bowel syndrome. Curr Opin Infect Dis 24:503–508
DuPont AW, DuPont HL (2011) The intestinal microbiota and chronic disorders of the gut. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 8:523–531
Cremon C, Gargano L, Morselli-Labate AM, Santini D, Cogliandro RF, De Giorgio R, Stanghellini V, Corinaldesi R, Barbara G (2009) Mucosal immune activation in irritable bowel syndrome: gender-dependence and association with digestive symptoms. Am J Gastroenterol 104:392–400
Spiller R, Garsed K (2009) Postinfectious irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 136:1979–1988
Kassinen A, Krogius-Kurikka L, Mäkivuokko H, Rinttilä T, Paulin L, Corander J, Malinen E, Apajalahti J, Palva A (2007) The fecal microbiota of irritable bowel syndrome patients differs significantly from that of healthy subjects. Gastroenterology 133:24–33
Krogius-Kurikka L, Lyra A, Malinen E, Aarnikunnas J, Tuimala J, Paulin L, Mäkivuokko H, Kajander K, Palva A (2009) Microbial community analysis reveals high level phylogenetic alterations in the overall gastrointestinal microbiota of diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome sufferers. BMC Gastroenterol 9:95
Lyra A, Rinttilä T, Nikkilä J, Krogius-Kurikka L, Kajander K, Malinen E, Mättö J, Mäkelä L, Palva A (2009) Diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome distinguishable by 16S rRNA gene phylotype quantification. World J Gastroenterol 15:5936–5945
Tana C, Umesaki Y, Imaoka A, Handa T, Kanazawa M, Fukudo S (2010) Altered profiles of intestinal microbiota and organic acids may be the origin of symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil 22:512–519
McKernan DP, Gaszner G, Quigley EM, Cryan JF, Dinan TG (2011) Altered peripheral toll- like receptor responses in the irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 33:1045–1052
Lee KJ, Tack J (2010) Altered intestinal microbiota in irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil 22:493–498
Agrawal A, Whorwell PJ (2008) Review article: abdominal bloating and distension in functional gastrointestinal disorders–epidemiology and exploration of possible mechanisms. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 27:2–10
Barbara G, De Giorgio R, Stanghellini V, Cremon C, Salvioli B, Corinaldesi R (2004) New pathophysiological mechanisms in irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 20:1–9
Walker EA, Gelfand AN, Gelfand MD, Green C, Katon WJ (1996) Chronic pelvic pain and gynecological symptoms in women with irritable bowel syndrome. J Psychosom Obstet Gynaecol 17:39–46
Ozdil K, Sahin A, Calhan T, Kahraman R, Nigdelioglu A, Akyuz U, Sokmen HM (2011) The frequency of microscopic and focal active colitis in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. BMC Gastroenterol 11:96
Stoicescu A, Andrei M, Becheanu G, Stoicescu M, Nicolaie T, Diculescu M (2012) Microscopic colitis and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth–diagnosis behind the irritable bowel syndrome? Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi 116:766–772
Svedberg P, Johansson S, Wallander MA, Hamelin B, Pedersen NL (2002) Extra-intestinal manifestations associated with irritable bowel syndrome: a twin study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 16:975–983
Di Berardino F, Filipponi E, Alpini D, O’Bryan T, Soi D, Cesarani A (2013) Ménière disease and gluten sensitivity: Recovery after a gluten-free diet. Am J Otolaryngol 2013 Jan 29. pii: S0196-0709(13)00012-4. doi:10.1016/j.amjoto.2012.12.019
Barghi M (2005) The relation of enuresis and irritable bowel syndrome with premature ejaculation: a preliminary report. Urol J 2:201–205
Creed F, Guthrie E (1987) Psychological factors in the irritable bowel syndrome. Gut 28:1307–1318
Ohman L, Simrén M (2010) Pathogenesis of IBS: role of inflammation, immunity and neuroimmune interactions. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 7:163–173
El-Salhy M (2012) Irritable bowel syndrome: diagnosis and pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 18:5151–5163
El-Salhy M, Wendelbo IH, Gundersen D (2013) Reduced chromogranin a cell density in the ileum of patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Mol Med Rep 7:1241–1244
Wahnschaffe U, Ullrich R, Riecken EO, Schulzke JD (2001) Celiac disease-like abnormalities in a subgroup of patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 121:1329–1338
Cash BD, Rubenstein JH, Young PE, Gentry A, Nojkov B, Lee D, Andrews AH, Dobhan R, Chey WD (2011) The prevalence of celiac disease among patients with nonconstipated irritable bowel syndrome is similar to controls. Gastroenterology 141:1187–1193
Ford AC, Chey WD, Talley NJ, Malhotra A, Spiegel BM, Moayyedi P (2009) Yield of diagnostic tests for celiac disease in individuals with symptoms suggestive of irritable bowel syndrome: systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med 169:651–658
Posserud I, Ersryd A, Simrén M (2006) Functional findings in irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 12:2830–2838
Larsson MB, Tillisch K, Craig AD, Engström M, Labus J, Naliboff B, Lundberg P, Ström M, Mayer EA, Walter SA (2012) Brain responses to visceral stimuli reflect visceral sensitivity thresholds in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 142(463–472):e3
Thompson JJ, Elsenbruch S, Harnish MJ, Orr WC (2002) Autonomic functioning during REM sleep differentiates IBS symptom subgroups. Am J Gastroenterol 97:3147–3153
Robert JJ, Orr WC, Elsenbruch S (2004) Modulation of sleep quality and autonomic functioning by symptoms of depression in women with irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Dis Sci 49:1250–1258
Robert JJ, Elsenbruch S, Orr WC (2006) Sleep-related autonomic disturbances in symptom subgroups of women with irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Dis Sci 51:2121–2127
Jarrett ME, Burr RL, Cain KC, Rothermel JD, Landis CA, Heitkemper MM (2008) Autonomic nervous system function during sleep among women with irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Dis Sci 53:694–703
Spetalen S, Sandvik L, Blomhoff S, Jacobsen MB (2008) Autonomic function at rest and in response to emotional and rectal stimuli in women with irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Dis Sci 53:1652–1659
Mazurak N, Seredyuk N, Sauer H, Teufel M, Enck P (2012) Heart rate variability in the irritable bowel syndrome: a review of the literature. Neurogastroenterol Motil 24:206–216
Gill SR, Pop M, Deboy RT, Eckburg PB, Turnbaugh PJ, Samuel BS, Gordon JI, Relman DA, Fraser-Liggett CM, Nelson KE (2006) Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut microbiome. Science 312:1355–1359
Hopkins MJ, Sharp R, Macfarlane GT (2001) Age and disease related changes in intestinal bacterial populations assessed by cell culture, 16S rRNA abundance, and community cellular fatty acid profiles. Gut 48:198–205
Enck P, Zimmermann K, Rusch K, Schwiertz A, Klosterhalfen S, Frick JS (2009) The effects of ageing on the colonic bacterial microflora in adults. Z Gastroenterol 47:653–658
Woodmansey EJ (2007) Intestinal bacteria and ageing. J Appl Microbiol 102:1178–1186
Guigoz Y, Doré J, Schiffrin EJ (2008) The inflammatory status of old age can be nurtured from the intestinal environment. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 11:13–20
Hébuterne X (2003) Gut changes attributed to ageing: effects on intestinal microflora. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 6:49–54
Biagi E, Nylund L, Candela M, Ostan R, Bucci L, Pini E, Nikkïla J, Monti D, Satokari R, Franceschi C, Brigidi P, De Vos W (2010) Through ageing, and beyond: gut microbiota and inflammatory status in seniors and centenarians. PLoS ONE 5:e10667
Vazquez-Roque MI, Camilleri M, Smyrk T, Murray JA, O’Neill J, Carlson P, Lamsam J, Eckert D, Janzow D, Burton D, Ryks M, Rhoten D, Zinsmeister AR (2012) Association of HLA-DQ gene with bowel transit, barrier function, and inflammation in irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 303:G1262–G1269
Van Oudenhove L, Demyttenaere K, Tack J, Aziz QB (2004) Central nervous system involvement in functional gastrointestinal disorders. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 18:663–680
Vasina V, Barbara G, Talamonti L, Stanghellini V, Corinaldesi R, Tonini M, De Ponti F, De Giorgio R (2006) Enteric neuroplasticity evoked by inflammation. Auton Neurosci 126–127:264–272
Barbara G (2006) Mucosal barrier defects in irritable bowel syndrome. Who left the door open? Am J Gastroenterol 101:1295–1298
Macpherson AJ, McCoy KD, Johansen FE, Brandtzaeg P (2008) The immune geography of IgA induction and function. Mucosal Immunol 1:11–22
Bauer H, Horowitz RE, Levenson SM, Popper H (1963) The response of the lymphatic tissue to the microbial flora. Studies on germ free mice. Am J Pathol 42:471–483
Bauer H, Paronetto F, Burns WA, Einheber A (1966) The enhancing effect of the microbial flora on macrophage function and the immune response. A study in germ free mice. J Exp Med 123:1013–1024
Tsuda M, Hosono A, Yanagibashi T, Kihara-Fujioka M, Hachimura S, Itoh K, Hirayama K, Takahashi K, Kaminogawa S (2010) Intestinal commensal bacteria promote T cell hyporesponsiveness and down-regulate the serum antibody responses induced by dietary antigen. Immunol Lett 132:45–52
Tobias PS, Soldau K, Gegner JA, Mintz D, Ulevitch RJ (1995) Lipopolysaccharide binding protein-mediated complexation of lipopolysaccharide with soluble CD14. J Biol Chem 270:10482–10488
Beutler B, Hoebe K, Du X, Ulevitch RJ (2003) How we detect microbes and respond to them: the Toll-like receptors and their transducers. J Leukoc Biol 74:479–485
Baldwin AS Jr (1996) The NF-κB and IκB proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol 14:649–683
Zahorska-Markiewicz B, Janowska J, Olszanecka-Glinianowicz M, Zurakowski (2000) A Serum concentrations of TNF-α and soluble TNF-α receptors in obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24:1392–1395
El-Wakkad A, Hassan N-M, Sibaii H, El-Zayat SR (2013) Proinflammatory, anti- inflammatory cytokines and adiponkines in students with central obesity. Cytokine 61:682–687
Nov O, Shapiro H, Ovadia H, Tarnovscki T, Dvir I, Shemesh E, Kovsan J, Shelef I, Carmi Y, Voronov E, Apte RN, Lewis E, Haim Y, Konrad D, Bashan N, Rudich A (2013) Interleukin-1β regulates fat-liver crosstalk in obesity by auto-paracrine modulation of adipose tissue inflammation and expandability. PLoS ONE 8:e53626
Uysal KT, Wiesbrock SM, Marino MW, Hotamisligil GS (1997) Protection from obesity- induced insulin resistance in mice lacking TNF-α function. Nature 389:610–614
Pagano G, Pacini G, Musso G, Gambino R, Mecca F, Depetris N, Cassader M, David E, Cavallo-Perin P, Rizzetto M (2002) Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome: further evidence for an etiologic association. Hepatology 35:367–372
Shanab AA, Scully P, Crosbie O, Buckley M, O’Mahony L, Shanahan F, Gazareen S, Murphy E, Quigley EM (2011) Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: association with toll-like receptor 4 expression and plasma levels of interleukin 8. Dig Dis Sci 56:1524–1534
Neal MD, Leaphart C, Levy R, Prince J, Billiar TR, Watkins S, Li J, Cetin S, Ford H, Schreiber A, Hackam DJ (2006) Enterocyte TLR4 mediates phagocytosis and translocation of bacteria across the intestinal barrier. J Immunol 176:3070–3079
Kim KA, Gu W, Lee IA, Joh EH, Kim DH (2012) High fat diet-induced gut microbiota exacerbates inflammation and obesity in mice via the TLR4 signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 7:e47713
Cani PD, Amar J, Iglesias MA, Poggi M, Knauf C, Bastelica D, Neyrinck AM, Fava F, Tuohy KM, Chabo C, Waget A, Delmée E, Cousin B, Sulpice T, Chamontin B, Ferrières J, Tanti JF, Gibson GR, Casteilla L, Delzenne NM, Alessi MC, Burcelin R (2007) Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 56:1761–1772
Ibeakanma C, Ochoa-Cortes F, Miranda-Morales M, McDonald T, Spreadbury I, Cenac N, Cattaruzza F, Hurlbut D, Vanner S, Bunnett N, Vergnolle N, Vanner S (2011) Brain-gut interactions increase peripheral nociceptive signaling in mice with postinfectious irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 141(2098–2108):e5
Tougas G (1999) The autonomic nervous system in functional bowel disorders. Can J Gastroenterol 13 Suppl A:15A-17A
Holzer P, Schicho R, Holzer-Petsche U, Lippe IT (2001) The gut as a neurological organ. Wien Klin Wochenschr 113:647–660
Mertz HR (2003) Overview of functional gastrointestinal disorders: dysfunction of the brain- gut axis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 32:463–476
Delvaux M (2004) Alterations of sensori-motor functions of the digestive tract in the pathophysiology of irritable bowel syndrome. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 18:747–771
Mulak A, Bonaz B (2004) Irritable bowel syndrome: a model of the brain-gut interactions. Med Sci Monit 10:RA55-RA62
Forsythe P, Kunze WA, Bienenstock J (2012) On communication between gut microbes and the brain. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 28:557–562
Forsythe P, Kunze WA (2013) Voices from within: gut microbes and the CNS. Cell Mol Life Sci 70:55–69
Crowell MD, Harris L, Jones MP, Chang L (2005) New insights into the pathophysiology of irritable bowel syndrome: implications for future treatments. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 7:272–279
Hosoi T, Okuma Y, Nomura Y (2000) Electrical stimulation of afferent vagus nerve induces IL-1beta expression in the brain and activates HPA axis. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 279:R141–R147
Maier SF, Goehler LE, Fleshner M, Watkins LR (1998) The role of the vagus nerve in cytokine-to-brain communication. Ann NY Acad Sci 840:289–300
Berthoud HR, Kressel M, Raybould HE, Neuhuber WL (1991) Vagal sensors in the rat duodenal mucosa: distribution and structure as revealed by in vivo tracing. Anat Embryol 191:203–212
Rogers RC, McTigue DM, Hermann GE (1995) Vagovagal reflex control of digestion: afferent modulation by neural and “endoneurocrine” factors. Am J Physiol 268:G1–G10
Zhuo H, Ichikawa H, Helke CJ (1997) Neurochemistry of the nodose ganglion. Prog Neurobiol 52:79–107
Browning KN (2003) Excitability of nodose ganglion cells and their role in vago-vagal reflex control of gastrointestinal function. Curr Opin Pharmacol 3:613–617
Browning KN, Mendelowitz D (2003) Musings on the wanderer: what’s new in our understanding of vago-vagal reflexes?: iI Integration of afferent signaling from the viscera by the nodose ganglia. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 284:G8–G14
Browning KN, Travagli RA (2010) Plasticity of vagal brainstem circuits in the control of gastric function. Neurogastroenterol Motil 22:1154–1163
Travagli RA, Hermann GE, Browning KN, Rogers RC (2006) Brainstem circuits regulating gastric function. Annu Rev Physiol 68:279–305
Sternberg EM (2006) Neural regulation of innate immunity: a coordinated nonspecific response to pathogens. Nat Rev Immunol 6:318–328
Tracey KJ, Czura CJ, Ivanova S (2001) Mind over immunity. Faseb J 15:1575–1576
Tracey KJ (2002) The inflammatory reflex. Nature 420:853–859
Tracey KJ (2007) Physiology and immunology of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. J Clin Invest 117:289–296
Borovikova LV, Ivanova S, Zhang M, Yang H, Yang, Botchkina GI, Watkins LR, Wang H, Abumrad N, Eaton JW, Tracey KJ (2000) Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature 405:458–462
Ghia JE, Blennerhassett P, Kumar-Ondiveeran H, Verdu EF, Collins SM (2006) The vagus nerve: a tonic inhibitory influence associated with inflammatory bowel disease in a murine model. Gastroenterology 131:1122–1130
Bernik TR, Friedman SG, Ochani M, DiRaimo R, Ulloa L, Yang H, Sudan S, Czura CJ, Ivanova SM, Tracey KJ (2002) Pharmacological stimulation of the cholinergic antiinflammatory pathway. J Exp Med 195:781–788
Borovikova LV, Ivanova S, Nardi D, Zhang M, Yang H, Ombrellino M, Tracey KJ (2000) Role of vagus nerve signaling in CNI-1493-mediated suppression of acute inflammation. Auton Neurosci 85:141–147
Pavlov VA, Tracey KJ (2005) The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Brain Behav Immun 19:493–499
Pavlov VA, Ochani M, Yang LH, Gallowitsch-Puerta M, Ochani K, Lin X, Levi J, Parrish WR, Rosas-Ballina M, Czura CJ, Larosa GJ, Miller EJ, Tracey KJ, Al-Abed Y (2007) Selective alpha7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist GTS-21 improves survival in murine endotoxemia and severesepsis. Crit Care Med 35:1139–1144
Wang H, Yu M, Ochani M, Amella CA, Tanovic M, Susarla S, Li JH, Wang H, Yang H, Ulloa L, Al-Abed Y, Czura CJ, Tracey KJ (2003) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 subunit is an essential regulator of inflammation. Nature 421:384–388
Matsunaga K, Klein TW, Friedman H, Yamamoto Y (2001) Involvement of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in suppression of antimicrobial activity and cytokine responses of alveolar macrophages to Legionella pneumophila infection by nicotine. J Immunol 167:6518–6524
Galvis G, Lips KS, Kummer W (2006) Expression of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on murine alveolar macrophages. J Mol Neurosci 30:107–108
Karimi K, Bienenstock J, Wang L, Forsythe P (2010) The vagus nerve modulates CD4 + T cell activity. Brain Behav Immun 24:316–323
Huston JM, Ochani M, Rosas-Ballina M, Liao H, Ochani K, Pavlov VA, Gallowitsch-Puerta M, Ashok M, Czura CJ, Foxwell B, Tracey KJ, Ulloa L (2006) Splenectomy inactivates the cholinergic antiinflammatory pathway during lethal endotoxemia and polymicrobial sepsis. J Exp Med 203:1623–1628
Huston JM, Rosas-Ballina M, Xue X, Dowling O, Ochani K, Ochani M, Yeboah MM, Chatterjee PK, Tracey KJ, Metz CN (2009) Cholinergic neural signals to the spleen down-regulate leukocyte trafficking via CD11b. J Immunol 183:552–559
Hansen MK, Taishi P, Chen Z, Krueger JM (1998) Vagotomy blocks the induction of interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) mRNA in the brain of rats in response to systemic IL-1beta. J Neurosci 18:2247–2253
Hansen MK, Nguyen KT, Goehler LE, Gaykema RP, Fleshner M, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2000) Effects of vagotomy on lipopolysaccharide-induced brain interleukin-1beta protein in rats. Auton Neurosci 85:119–126
Van der Zanden EP, Boeckxstaens GE, De Jonge WJ (2009) The vagus nerve as a modulator of intestinal inflammation. Neurogastroenterol Motil 21:6–17
Woiciechowsky C, Schöning B, Daberkow N, Asche K, Stoltenburg G, Lanksch WR, Volk HD (1999) Brain-IL-1beta induces local inflammation but systemic anti-inflammatory response through stimulation of bothhypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and sympathetic nervous system. Brain Res 816:563–571
Puder JJ, Freda PU, Goland RS, Wardlaw SL (2001) Estrogen modulates the hypothalamic- pituitary-adrenal and inflammatory cytokine responses to endotoxin in women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:2403–2408
Beishuizen A, Thijs LG (2003) Endotoxin and the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. J Endotoxin Res 9:3–24
Hermann GE, Holmes GM, Rogers RC (2005) TNF(alpha) modulation of visceral and spinal sensory processing. Curr Pharm Des 11:1391–1409
Hermann GE, Rogers RC (2008) TNFalpha: a trigger of autonomic dysfunction. Neuroscientist 14:53–67
van Westerloo DJ, Giebelen IA, Meijers JC, Daalhuisen J, de Vos AF, Levi M, van der Poll T (2006) Vagus nerve stimulation inhibits activation of coagulation and fibrinolysis during endotoxemia in rats. J Thromb Haemost 4:1997–2002
Gidron Y, Kupper N, Kwaijtaal M, Winter J, Denollet J (2007) Vagus-brain communication in atherosclerosis- related inflammation: a neuroimmunomodulationperspective of CAD. Atherosclerosis 195:e1–e9
Erdos B, Kirichenko N, Whidden M, Basgut B, Woods M, Cudykier I, Tawil R, Scarpace PJ, Tumer N (2011) Effect of age on high-fat diet-induced hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 301:H164–H172
Adebakin A, Bradley J, Gümüsgöz S, Waters EJ, Lawrence CB (2012) Impaired satiation and increased feeding behaviour in the triple-transgenic Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. PLoS ONE 7:e45179
Knight EM, Brown TM, Gümüsgöz S, Smith JC, Waters EJ, Allan SM, Lawrence CB (2013) Age-related changes in core body temperature and activity in triple-transgenic Alzheimer’s disease (3xTgAD) mice. Dis Model Mech 6:160–170
Almado CE, Machado BH, Leão RM (2012) Chronic intermittent hypoxia depresses afferent neurotransmission in NTS neurons by a reduction in the number of active synapses. J Neurosci 32:16736–16746
Kwan CL, Diamant NE, Pope G, Mikula K, Mikulis DJ, Davis KD (2005) Abnormal forebrain activity in functional bowel disorder patients with chronic pain. Neurology 65:1268–1277
Chen JY, Blankstein U, Diamant NE, Davis KD (2011) White matter abnormalities in irritable bowel syndrome and relation to individual factors. Brain Res 1392:121–131
Pavlov VA, Wang H, Czura CJ, Friedman SG, Tracey KJ (2003) The cholinergic anti- inflammatory pathway: a missing link in neuroimmunomodulation. Mol Med 9:125–134
Pavlov VA, Tracey KJ (2004) Neural regulators of innate immune responses and inflammation. Cell Molec Life Sci 61:2322–2331
Riley TP, Neal-McKinney JM, Buelow DR, Konkel ME, Simasko SM (2013) Capsaicin- sensitive vagal afferent neurons contribute to the detection of pathogenic bacterial colonization in the gut. J Neuroimmunol 257:36–45
Luyer MD, Greve JW, Hadfoune M, Jacobs JA, Dejong CH, Buurman WA (2005) Nutritional stimulation of cholecystokinin receptors inhibits inflammation via the vagus nerve. J Exp Med 202:1023–1029
Liu CY, Mueller MH, Grundy D, Kreis ME (2007) Vagal modulation of intestinal afferent sensitivity to systemic LPS in the rat. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 292:G1213–G1220
Yilmaz MS, Goktalay G, Millington WR, Myer BS, Cutrera RA, Feleder C (2008) Lipopolysaccharide-induced hypotension is mediated by a neural pathway involving the vagus nerve, the nucleus tractus solitarius and alpha-adrenergic receptors in the preoptic anterior hypothalamic area. J Neuroimmunol 203:39–49
Krstic D, Madhusudan A, Doehner J, Vogel P, Notter T, Imhof C, Manalastas A, Hilfiker M, Pfister S, Schwerdel C, Riether C, Meyer U, Knuesel I (2012) Systemic immune challenges trigger and drive Alzheimer-like neuropathology in mice. J Neuroinflammation 9:151
Krstic D, Knuesel I (2013) Deciphering the mechanism underlying late-onset Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol 9:25–34
Hoozemans JJ, Rozemuller AJ, van Haastert ES, Eikelenboom P, van Gool WA (2011) Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease wanes with age. J Neuroinflammation 8:171
Ahluwalia N, Vellas B (2003) Immunologic and inflammatory mediators and cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 23:103–115
Lin HB, Yang XM, Li TJ, Cheng YF, Zhang HT, Xu JP (2009) Memory deficits and neurochemical changes induced by C-reactive protein in rats: implication in Alzheimer’s disease. Psychopharmacology 204:705–714
Bhamra MS, Ashton NJ (2012) Finding a pathological diagnosis for Alzheimer’s disease: are inflammatory molecules the answer? Electrophoresis 33:3598–3607
Hall JR, Wiechmann AR, Johnson LA, Edwards M, Barber RC, Winter AS, Singh M, O’Bryant SE (2013) Biomarkers of vascular risk, systemic inflammation, and microvascular pathology and neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 35:363–371
Ghosh S, Wu MD, Shaftel SS, Kyrkanides S, LaFerla FM, Olschowka JA, O’Banion MK (2013) Sustained interleukin-1β overexpression exacerbates tau pathology despite reduced amyloid burden in an Alzheimer’s mouse model. J Neurosci 33:5053–5064
Takeda S, Sato N, Ikimura K, Nishino H, Rakugi H, Morishita R (2013) Increased blood- brain barrier vulnerability to systemic inflammation in an Alzheimer disease mouse model. Neurobiol Aging 34:2064–2070
Zhao SJ, Guo CN, Wang MQ, Chen WJ, Zhao YB (2012) Serum levels of inflammation factors and cognitive performance in amnestic mild cognitive impairment: a Chinese clinical study. Cytokine 57:221–225
Sawada M, Imamura K, Nagatsu T (2006) Role of cytokines in inflammatory process in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm Suppl 70:373–381
Browne TC, McQuillan K, McManus RM, O’Reilly JA, Mills KH, Lynch MA (2013) IFN-γ production by amyloid β-specific Th1 cells promotes microglial activation and increases plaque burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Immunol 190:2241–2251
Probert L, Akassoglou K, Kassiotis G, Pasparakis M, Alexopoulou L, Kollias G (1997) TNF- alpha transgenic and knockout models of CNS inflammation and degeneration. J Neuroimmunol 72:137–141
Koyama A, O’Brien J, Weuve J, Blacker D, Metti AL, Yaffe K (2013) The role of peripheral inflammatory markers in dementia and Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analysis. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 68:433–440
Guo JT, Yu J, Grass D, de Beer FC, Kindy MS (2002) Inflammation-dependent cerebral deposition of serum amyloid a protein in a mouse model of amyloidosis. J Neurosci 22:5900–5909
Lee JW, Lee YK, Yuk DY, Choi DY, Ban SB, Oh KW, Hong JT (2008) Neuro-inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide causes cognitive impairment through enhancement of beta-amyloid generation. J Neuroinflammation 5:37
Hirose Y, Imai Y, Nakajima K, Takemoto N, Toya S, Kohsaka S (1994) Glial conditioned medium alters the expression of amyloid precursor protein in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 198:504–509
Buxbaum JD, Oishi M, Chen HI, Pinkas-Kramarski R, Jaffe EA, Gandy SE, Greengard P (1992) Cholinergic agonists and interleukin 1 regulate processing and secretion of the Alzheimer beta/A4 amyloid protein precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:10075–10078
Sastre M, Dewachter I, Landreth GE, Willson TM, Klockgether T, van Leuven F, Heneka MT (2003) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonists modulate immunostimulated processing of amyloid precursor protein through regulation of beta-secretase. J Neurosci 23:9796–9804
Blasko I, Marx F, Steiner E, Hartmann T, Grubeck-Loebenstein B (1999) TNFalpha plus IFNgamma induce the production of Alzheimer beta-amyloid peptides and decrease the secretion of APPs. FASEB J 13:63–68
Frings L, Spehl TS, Weber WA, Hüll M, Meyer PT (2013) Amyloid-β load predicts medial temporal lobe dysfunction in alzheimer dementia. J Nucl Med 54:1909–1914
Rodríguez JJ, Noristani HN, Hilditch T, Olabarria M, Yeh CY, Witton J, Verkhratsky A (2013) Increased densities of resting and activated microglia in the dentate gyrus follow senile plaque formation in the CA1 subfield of the hippocampus in the triple transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 552:129–134
Wright AL, Zinn R, Hohensinn B, Konen LM, Beynon SB, Tan RP, Clark IA, Abdipranoto A, Vissel B (2013) Neuroinflammation and neuronal loss precede Aβ plaque deposition in the hAPP-J20 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 8:e59586
Kahn MS, Kranjac D, Alonzo CA, Haase JH, Cedillos RO, McLinden KA, Boehm GW, Chumley MJ (2012) Prolonged elevation in hippocampal Aβ and cognitive deficits following repeated endotoxin exposure in the mouse. Behav Brain Res 229:176–184
Bossù P, Cutuli D, Palladino I, Caporali P, Angelucci F, Laricchiuta D, Gelfo F, De Bartolo P, Caltagirone C, Petrosini L (2012) A single intraperitoneal injection of endotoxin in rats induces long-lasting modifications in behavior and brain protein levels of TNF-α and IL- 18. J Neuroinflammation 9:101
Moore AH, Wu M, Shaftel SS, Graham KA, O’Banion MK (2009) Sustained expression of interleukin-1beta in mouse hippocampus impairs spatial memory. Neuroscience 164:1484–1495
Gasparini L, Rusconi L, Xu H, del Soldato P, Ongini E (2004) Modulation of beta-amyloid metabolism by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in neuronal cell cultures. J Neurochem 88:337–348
Shaw KN, Commins S, O’Mara SM (2001) Lipopolysaccharide causes deficits in spatial learning in the water maze but not in BDNF expression in the rat dentate gyrus. Behav Brain Res 124:47–54
Sparkman NL, Martin LA, Calvert WS, Boehm GW (2005) Effects of intraperitoneal lipopolysaccharide on morris maze performance in year-old and 2-month-old female C57BL/6 J mice. Behav Brain Res 159:145–151
Turrin NP, Gayle D, Ilyin SE, Flynn MC, Langhans W, Schwartz GJ, Plata-Salamán CR (2001) Pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine mRNA induction in the periphery and brain following intraperitoneal administration of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Brain Res Bull 54:443–453
Lee YJ, Han SB, Nam SY, Oh KW, Hong JT (2010) Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Arch Pharm Res 33:1539–1556
Elsenbruch S, Rosenberger C, Enck P, Forsting M, Schedlowski M, Gizewski ER (2010) Affective disturbances modulate the neural processing of visceral pain stimuli in irritable bowel syndrome: an fMRI study. Gut 59:489–495
Rosenberger C, Thürling M, Forsting M, Elsenbruch S, Timmann D, Gizewski ER (2013) Contributions of the cerebellum to disturbed central processing of visceral stimuli in irritable bowel syndrome. Cerebellum 12:194–198
Mandolesi G, Musella A, Gentile A, Grasselli G, Haji N, Sepman H, Fresegna D, Bullitta S, De Vito F, Musumeci G, Di Sanza C, Strata P, Centonze D (2013) Interleukin-1β alters glutamate transmission at purkinje cell synapses in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. J Neurosci 33:12105–12121
Plata-Salamán CR, Ilyin SE, Gayle D, Flynn MC (1998) Gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial products induce differential cytokine profiles in the brain: analysis using an integrative molecular-behavioral in vivo model. Int J Mol Med 1:387–397
di Penta A, Moreno B, Reix S, Fernandez-Diez B, Villanueva M, Errea O, Escala N, Vandenbroeck K, Comella JX, Villoslada P (2013) Oxidative stress and proinflammatory cytokines contribute to demyelination and axonal damage in a cerebellar culture model of neuroinflammation. PLoS ONE 8:e54722
De Smet HJ, Baillieux H, De Deyn PP, Marien P, Paquier P (2007) The cerebellum and language: the story so far. Folia Phoniatr Logop 59:165–170
Strick PL, Dum RP, Fiez JA (2009) Cerebellum and nonmotor function. Annu Rev Neurosci 32:413–434
Hoffmann LC, Berry SD (2009) Cerebellar theta oscillations are synchronized during hippocampal theta-contingent trace conditioning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:21371–21376
Wikgren J, Nokia MS, Penttonen M (2010) Hippocampo-cerebellar theta band phase synchrony in rabbits. Neuroscience 165:1538–1545
Rochefort C, Lefort JM, Rondi-Reig L (2013) The cerebellum: a new key structure in the navigation system. Front Neural Circuits 7:35
Rochefort C, Arabo A, André M, Poucet B, Save E, Rondi-Reig L (2011) Cerebellum shapes hippocampal spatial code. Science 334(6054):385–389
Passot JB, Sheynikhovich D, Duvelle É, Arleo A (2012) Contribution of cerebellar sensorimotor adaptation to hippocampal spatial memory. PLoS ONE 7:e32560
Balsters JH, Whelan CD, Robertson IH, Ramnani N (2013) Cerebellum and cognition: evidence for the encoding of higher order rules. Cereb Cortex 23:1433–1443
Schmahmann JD, Sherman JC (1998) The cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome. Brain 121:561–579
Martin KL, Blizzard L, Wood AG, Srikanth V, Thomson R, Sanders LM, Callisaya ML (2013) Cognitive function, gait, and gait variability in older people: a population-based study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 68:726–732
Koch G, Mori F, Marconi B, Codecà C, Pecchioli C, Salerno S, Torriero S, Lo Gerfo E, Mir P, Oliveri M, Caltagirone C (2008) Changes in intracortical circuits of the human motor cortex following theta burst stimulation of the lateral cerebellum. Clin Neurophysiol 119:2559–2569
Koch G, Brusa L, Carrillo F, Lo Gerfo E, Torriero S, Oliveri M, Mir P, Caltagirone C, Stanzione P (2009) Cerebellar magnetic stimulation decreases levodopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson disease. Neurology 73:113–119
Di Lorenzo F, Martorana A, Ponzo V, Bonnì S, D’Angelo E, Caltagirone C, Koch G (2013) Cerebellar theta burst stimulation modulates short latency afferent inhibition in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Front Aging Neurosci 5:2
Finkelstein Y, Wolff M, Biegon A (1988) Brain acetylcholinesterase after parathion poisoning: a comparative quantitative histochemical analysis post-mortem. Toxicology 49:165–169
Turner JR, Ortinski PI, Sherrard RM, Kellar KJ (2011) Cerebellar nicotinic cholinergic receptors are intrinsic to the cerebellum: implications for diverse functional roles. Cerebellum 10:748–757
D’Angelo E, Casali S (2012) Seeking a unified framework for cerebellar function and dysfunction: from circuit operations to cognition. Front Neural Circuits 6:116
Okamura N, Funaki Y, Tashiro M, Kato M, Ishikawa Y, Maruyama M, Ishikawa H, Meguro K, Iwata R, Yanai K (2008) In vivo visualization of donepezil binding in the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Br J Clin Pharmacol 65:472–479
Larner AJ (1997) The cerebellum in Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 8:203–209
Sjöbeck M, Englund E (2001) Alzheimer’s disease and the cerebellum: a morphologic study on neuronal and glial changes. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 12:211–218
Stępień T, Wierzba-Bobrowicz T, Lewandowska E, Szpak G (2012) Morphological and quantitative analysis of cerebellar cortical cells in Alzheimer’s disease. Folia Neuropathol 50:250–260
Mavroudis IA, Fotiou DF, Adipepe LF, Manani MG, Njau SD, Psaroulis D, Costa VG, Baloyannis SJ (2010) Morphological changes of the human purkinje cells and deposition of neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles on the cerebellar cortex of Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen 25:585–591
Wegiel J, Wisniewski HM, Dziewiatkowski J, Badmajew E, Tarnawski M, Reisberg B, Mlodzik B, De Leon MJ, Miller DC (1999) Cerebellar atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease- clinicopathological correlations. Brain Res 818:41–50
Mattiace LA, Davies P, Yen SH, Dickson DW (1990) Microglia in cerebellar plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 80:493–498
Baldaçara L, Borgio JG, Moraes WA, Lacerda AL, Montaño MB, Tufik S, Bressan RA, Ramos LR, Jackowski AP (2011) Cerebellar volume in patients with dementia. Rev Bras Psiquiatr 33:122–129
Andersen K, Andersen BB, Pakkenberg B(2012) Stereological quantification of the cerebellum in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 33:197.e11-e20
Thomann PA, Schlafer C, Seidl U, Santos VD, Essig M, Schroder J (2008) The cerebellum in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease—a structural MRI study. J Psychiatr Res 42:1198–1202
Möller C, Vrenken H, Jiskoot L, Versteeg A, Barkhof F, Scheltens P, van der Flier WM (2013) Different patterns of gray matter atrophy in early- and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 34:2014–2022
Chen J, Cohen ML, Lerner AJ, Yang Y, Herrup K (2010) DNA damage and cell cycle events implicate cerebellar dentate nucleus neurons as targets of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener 5:60
Hauser T, Schönknecht P, Thomann PA, Gerigk L, Schröder J, Henze R, Radbruch A, Essig M (2013) Regional cerebral perfusion alterations in patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease using dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI. Acad Radiol 20:705–711
McLaren DG, Sreenivasan A, Diamond EL, Mitchell MB, Van Dijk KR, Deluca AN, O’Brien JL, Rentz DM, Sperling RA, Atri A (2012) Tracking cognitive change over 24 weeks with longitudinal functional magnetic resonance imaging in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurodegener Dis 9:176–186
Drummond ES, Muhling J, Martins RN, Wijaya LK, Ehlert EM, Harvey AR (2013) Pathology associated with AAV mediated expression of beta amyloid or C100 in adult mouse hippocampus and cerebellum. PLoS ONE 8:e59166
Braak H, Braak E, Bohl J, Lang W (1989) Alzheimer’s disease: amyloid plaques in the cerebellum. J Neurol Sci 93:277–287
Joachim CL, Morris JH, Selkoe DJ (1989) Diffuse senile plaques occur commonly in the cerebellum in Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Pathol 135:309–319
Dickson DW, Wertkin A, Mattiace LA, Fier E, Kress Y, Davies P, Yen SH (1990) Ubiquitin immunoelectron microscopy of dystrophic neurites in cerebellar senile plaques of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 79:486–493
Fukutani Y, Cairns NJ, Rossor MN, Lantos PL (1996) Purkinje cell loss and astrocytosis in the cerebellum in familial and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 214:33–36
Cerejeira J, Firmino H, Vaz-Serra A, Mukaetova-Ladinska EB (2010) The neuroinflammatory hypothesis of delirium. Acta Neuropathol 119:737–754
Cunningham C (2011) Systemic inflammation and delirium:important co-factors in the progression of dementia. Biochem Soc Trans 39:945–953
Cunningham C, MacLullich AMJ (2013) At the extreme end of the psychoneuroimmunological spectrum: delirium as a maladaptive sickness behaviour response. Brain Behavior Immunity 28:1–13
Murray C, Sanderson DJ, Barkus C, Deacon RMJ, Rawlins JNP, Bannerman DM, Cunningham C (2012) Systemic inflammation induces acute working memory deficits in the primed brain: relevance for delirium. Neurobiol Aging 33(603–616):e3
Dunn AJ, Berridge CW (1990) Physiological and behavioral-responses to corticotropin- releasing factor administration—is Crf a mediator of anxiety or stress responses. Brain Res Rev 15:71–100
Vale W, Spiess J, Rivier C et al (1981) Characterization of a 41-residue ovine hypothalamic peptide that stimulates secretion of corticotropin and beta-endorphin. Science 213:1394–1397
Heim C, Nemeroff CB (2009) Neurobiology of posttraumatic stress disorder. CNS Spectr 14:13–24
Fukudo S (2007) Role of corticotropin-releasing hormone in irritable bowel syndrome and intestinal inflammation. J Gastroenterol 42:48–51
Stahl SM, Wise DD (2008) The potential role of a corticotropin-releasing factor receptor-1 antagonist in psychiatric disorders. CNS Spectr 13:467–472
Taché Y, Kiank C, Stengel A (2009) A role for corticotropin-releasing factor in functional gastrointestinal disorders. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 11:270–277
Labus JS, Hubbard CS, Bueller J, Ebrat B, Tillisch K, Chen M, Stains J, Dukes GE, Kelleher DL, Naliboff BD, Fanselow M, Mayer EA (2013) Impaired emotional learning and involvement of the corticotropin-releasing factor signaling system in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 145(1253–1261):e3
Hubbard CS, Labus JS, Bueller J et al (2011) Corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 1 antagonist alters regional activation and effective connectivity in an emotional-arousal circuit during expectation of abdominal pain. J Neurosci 31:12491–12500
Mayer EA (2000) The neurobiology of stress and gastrointestinal disease. Gut 47:861–869
Longstreth GF, Thompson WG, Chey WD, Houghton LA, Mearin F, Spiller RC (2006) Functional bowel disorders. Gastroenterology 130:1480–1491
Martinez V, Taché Y (2006) CRF1 receptors as a therapeutic target for irritable bowel syndrome. Curr Pharm Des 12:4071–4088
Phelps EA, O’Connor KJ, Gatenby JC, Gore JC, Grillon C, Davis M (2001) Activation of the left amygdala to a cognitive representation of fear. Nat Neurosci 4:437–441
Simpson JR, Drevets WC, Snyder AZ, Gusnard DA, Raichle ME (2001) Emotion-induced changes in human medial prefrontal cortex: II. During anticipatory anxiety. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:688–693
Straube T, Schmidt S, Weiss T, Mentzel HJ, Miltner WHR (2009) Dynamic activation of the anterior cingulate cortex during anticipatory anxiety. Neuroimage 44:975–981
Taché Y, Martinez V, Wang L, Million M (2004) CRF1 receptor signaling pathways are involved in stress-related alterations of colonic function and viscerosensitivity: implications for irritable bowel syndrome. Br J Pharmacol 141:1321–1330
Kamada N, Grace Chen G, Núñez G (2012) A complex microworld in the gut: harnessing pathogen-commensal relations. Nat Med 18:1190–1191
Christmas D, Steele JD, Tolomeo S, Eljamel MS, Matthews K (2013) Vagus nerve stimulation for chronic major depressive disorder: 12-month outcomes in highly treatment-refractory patients. J Affect Disord 2013 Jun 28. pii: S0165-0327(13)00459-X. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2013.05.080. [Epub ahead of print]
Marras CE, Chiesa V, De Benedictis A, Franzini A, Rizzi M, Villani F, Ragona F, Tassi L, Vignoli A, Freri E, Specchio N, Broggi G, Casazza M, Canevini MP (2013) Vagus nerve stimulation in refractory epilepsy: new indications and outcome assessment. Epilepsy Behav 28:374–378
Chen C, Zhang Y, Du Z, Zhang M, Niu L, Wang Y, Li J (2013) Vagal Efferent Fiber Stimulation Ameliorates Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cell Injury by Downregulating Inflammatory Responses. Inflammation 2013 Aug 4. [Epub ahead of print]
Hamann JJ, Ruble SB, Stolen C, Wang M, Gupta RC, Rastogi S, Sabbah HN (2013) Vagus nerve stimulation improves left ventricular function in a canine model of chronic heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. 2013 Jul 24 [Epub ahead of print]
Zhang Y, Popovic ZB, Bibevski S, Fakhry I, Sica DA, Van Wagoner DR, Mazgalev TN (2009) Chronic vagus nerve stimulation improves autonomic control and attenuates systemic inflammation and heart failure progression in a canine high-rate pacing model. Circ Heart Fail 2:692–699
Zhou H, Liang H, Li ZF, Xiang H, Liu W, Li JG (2013) Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates intestinal epithelial tight junctions disruption in endotoxemic mice through α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Shock 40:144–151
Zhang Y, Ilsar I, Sabbah HN, Ben David T, Mazgalev TN (2009) Relationship between right cervical vagus nerve stimulation and atrial fibrillation inducibility: therapeutic intensities do not increase arrhythmogenesis. Heart Rhythm 6:244–250
He W, Jing X, Wang X, Rong P, Li L, Shi H, Shang H, Wang Y, Zhang J, Zhu B (2013) Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation as a complementary therapy for pediatric epilepsy: a pilot trial. Epilepsy Behav 28:343–346
Groves DA, Brown VJ (2005) Vagal nerve stimulation: a review of its applications and potential mechanisms that mediate its clinical effects. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:493–500
Petrov T, Howarth AG, Krukoff TL, Stevenson BR (1994) Distribution of the tight junction- associated protein ZO-1 in circumventricular organs of the CNS. Mol Brain Res 21:235–246
Desson SE, Ferguson AV (2003) Interleukin 1β modulates rat subfornical organ neurons as a result of activation of a non-selective cationic conductance. J Physiol 550:113–122
Roth J, Harré EM, Rummel C, Gerstberger R, Hübschle T (2004) Signaling the brain in systemic inflammation: role of sensory circumventricular organs. Front Biosci 9:290–300
Ott D, Murgott J, Rafalzik S, Wuchert F, Schmalenbeck B, Roth J, Gerstberger R (2010) Neurons and glial cells of the rat organum vasculosum laminae terminalis directly respond to lipopolysaccharide and pyrogenic cytokines. Brain Res 1363:93–106
Smith PM, Ferguson AV (2010) Circulating signals as critical regulators of autonomic state– central roles for the subfornical organ. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 299:R405–R4015
Maolood N, Meister B (2009) Protein components of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) in the brainstem area postrema-nucleus tractus solitarius region. J Chem Neuroanat 37:182–195
Banks WA, Kastin AJ, Broadwell RD (1995) Passage of cytokines across the blood-brain barrier. NeuroImmunoModulation 2:241–248
Ilyin SE, Gayle D, Flynn MC, Plata-Salamán CR (1998) Interleukin-1beta system (ligand, receptor type I, receptor accessory protein and receptor antagonist), TNF-alpha, TGF- beta1 and neuropeptide Y mRNAs in specific brain regions during bacterial LPS-induced anorexia. Brain Res Bull 45:507–515
Belarbi K, Jopson T, Tweedie D, Arellano C, Luo W, Greig NH, Rosi S (2012) TNF-α protein synthesis inhibitor restores neuronal function and reverses cognitive deficits induced by chronic neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation 9:23
Sutinen EM, Pirttilä T, Anderson G, Salminen A, Ojala JO (2012) Pro-inflammatory interleukin-18 increases Alzheimer’s disease-associated amyloid-β production in human neuron-like cells. J Neuroinflammation 9:199
Chodobski A, Szmydynger-Chodobska J (2001) Choroid plexus: target for polypeptides and site of their synthesis. Microsc Res Tech 52:65–82
Szmydynger-Chodobska J, Gandy JR, Varone A, Shan R, Chodobski A (2013) Synergistic interactions between cytokines and avp at the blood-csf barrier result in increased chemokine production and augmented influx of leukocytes after brain injury. PLoS ONE 8:e79328
Erickson MA, Banks WA (2013) Blood–brain barrier dysfunction as a cause and consequence of Alzheimer’s disease. J Cerebr Blood Flow Metabol 33:1500–1513
Greenwood J, Heasman SJ, Alvarez JI, Prat A, Lyck R, Engelhardt B (2011) Leucocyte–endothelial cell crosstalk at the blood–brain barrier: a prerequisite for successful immune cell entry to the brain. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 37:24–39
Ryu JK, McLarnon JG (2009) A leaky blood-brain barrier, fibrinogen infiltration and microglial reactivity in inflamed Alzheimer’s disease brain. J Cell Mol Med 13:2911–2925
Rotem AY, Sperber AD, Krugliak P, Freidman B, Tal A, Tarasiuk A (2003) Polysomnographic and actigraphic evidence of sleep fragmentation in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Sleep 26:747–752
Kumar D, Thompson PD, Wingate DL, Vesselinova-Jenkins CK, Libby G (1992) Abnormal REM sleep in the irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 103:12–17
Shen F, Zhou H, Chen G, Song L, Liu Y, Yang L, Chen L, Li D (2011) Evaluation of Pittsburgh sleep quality index in assessing patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Chin J Gastroenterol 16:19–21
Gold AR, Broderick JE, Amin MM, Gold MS (2009) Inspiratory airflow dynamics during sleep in irritable bowel syndrome: a pilot study. Sleep Breath 13:397–407
Labus JS, Dinov ID, Jiang Z, Ashe-McNalley C, Zamanyan A, Shi Y, Hong JY, Gupta A, Tillisch K, Ebrat B, Hobel S, Gutman BA, Joshi S, Thompson PM, Toga AW, Mayer EA (2014) Irritable bowel syndrome in female patients is associated with alterations in structural brain networks. Pain 155:137–149
Jiang Z, Dinov ID, Labus J, Shi Y, Zamanyan A, Gupta A, Ashe-McNalley C, Hong JY, Tillisch K, Toga AW, Mayer EA (2013) Sex-related differences of cortical thickness in patients with chronic abdominal pain. PLoS One 8:e73932
Aizawa E, Sato Y, Kochiyama T, Saito N, Izumiyama M, Morishita J, Kanazawa M, Shima K, Mushiake H, Hongo M, Fukudo S (2012) Altered cognitive function of prefrontal cortex during error feedback in patients with irritable bowel syndrome, based on FMRI and dynamic causal modeling. Gastroenterology 143:1188–1198
Niddam DM, Tsai S-Y, Lu C-L, Ko C-W, Hsieh J-C (2011) Reduced hippocampal glutamate-glutamine levels in irritable bowel syndrome: preliminary findings using magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Am J Gastroenterol 106:1503–1511
Steinbach S, Reindl W, Kessel C, Ott R, Zahnert T, Hundt W, Heinrich P, Saur D, Huber W (2010) Olfactory and gustatory function in irritable bowel syndrome. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 267:1081–1087
Seminowicz DA, Labus JS, Bueller JA, Tillisch K, Naliboff BD, Bushnell MC, Mayer EA (2010) Regional gray matter density changes in brains of patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 139(48–57):e2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daulatzai, M.A. Chronic Functional Bowel Syndrome Enhances Gut-Brain Axis Dysfunction, Neuroinflammation, Cognitive Impairment, and Vulnerability to Dementia. Neurochem Res 39, 624–644 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1266-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1266-6